Chemical compatibility is a critical consideration in the selection of plastic materials for cosmetic jars. Cosmetic products often contain a wide variety of ingredients, some of which can interact with the packaging material if not properly matched. Understanding the chemical compatibility of plastic cosmetic jars ensures that the packaging maintains its integrity, and the cosmetic product remains safe and effective.
Plastic Types and Their Properties:
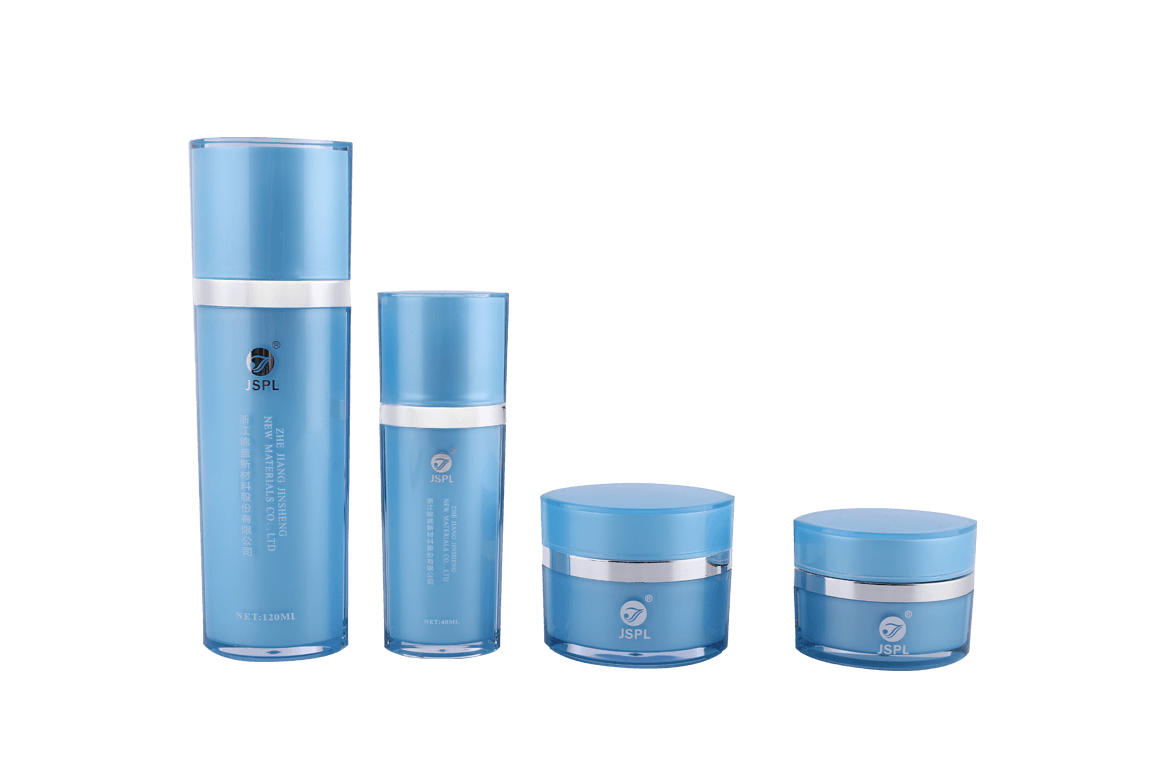
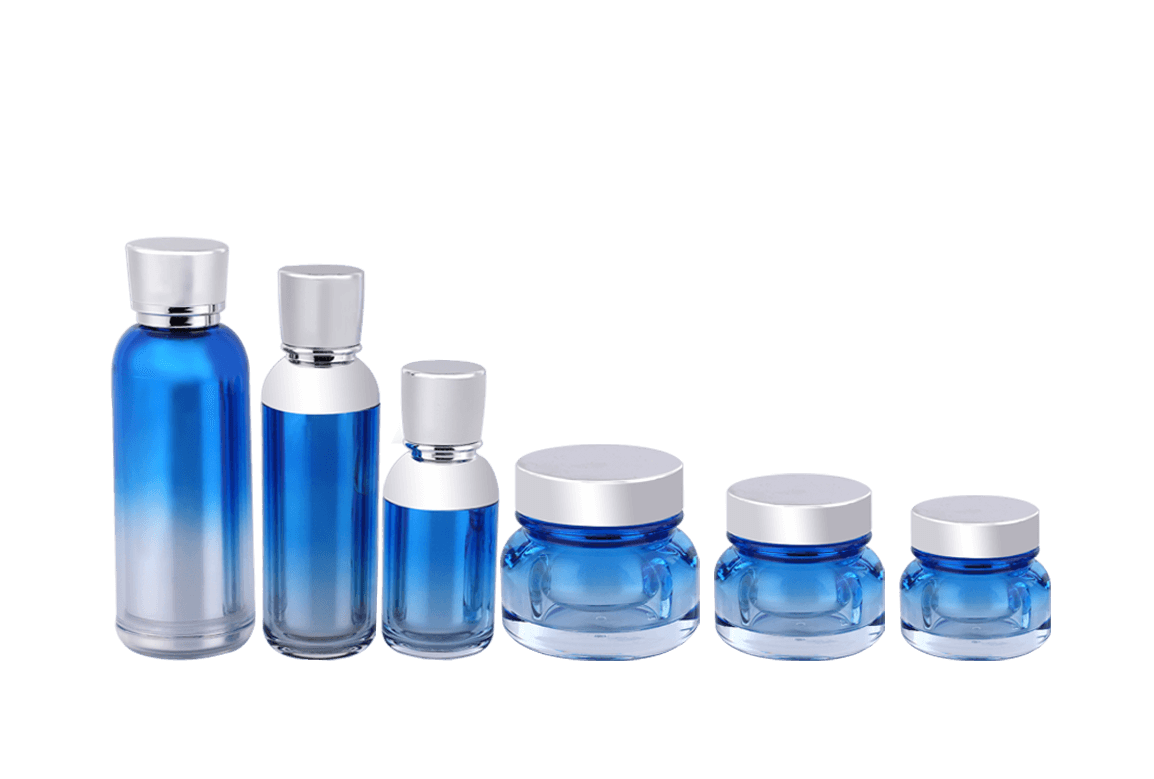
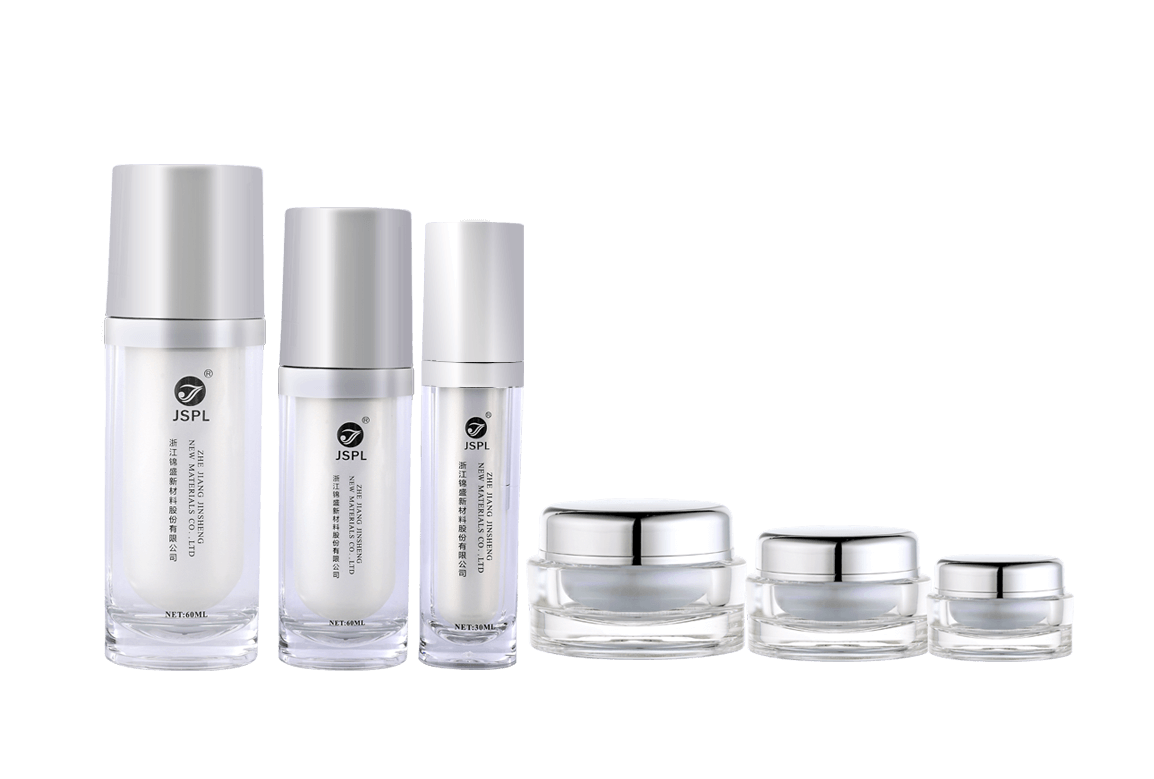
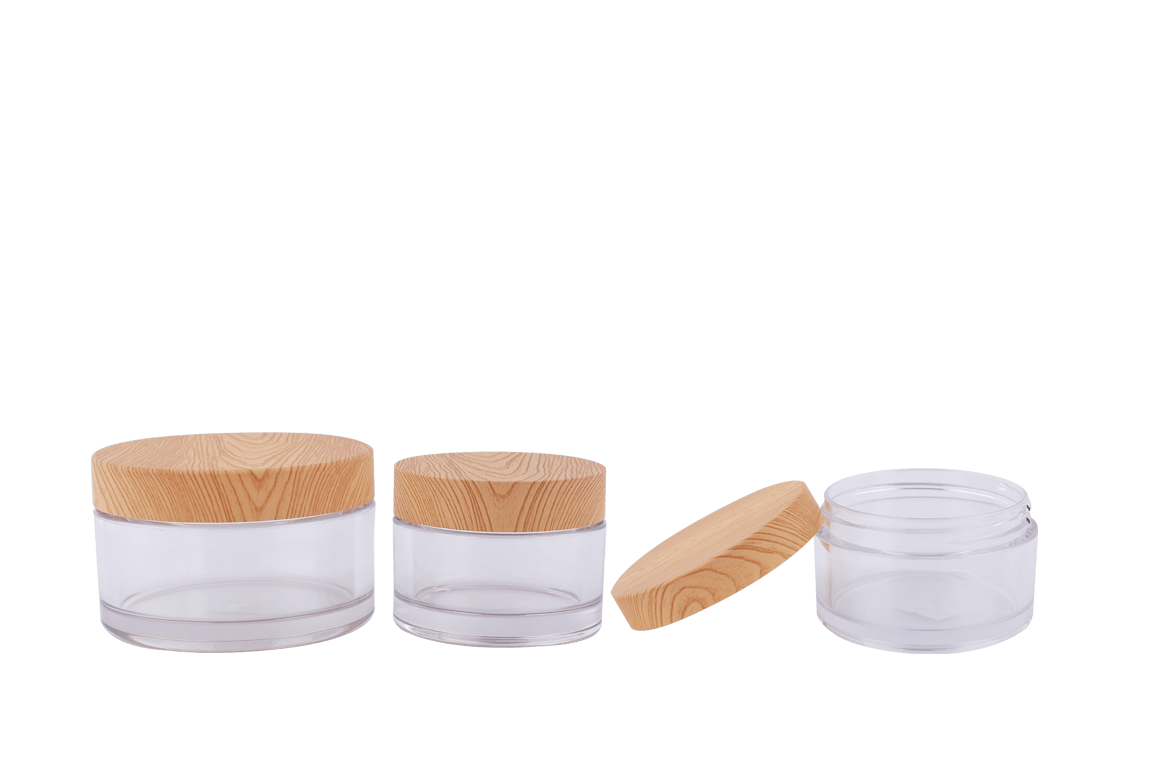
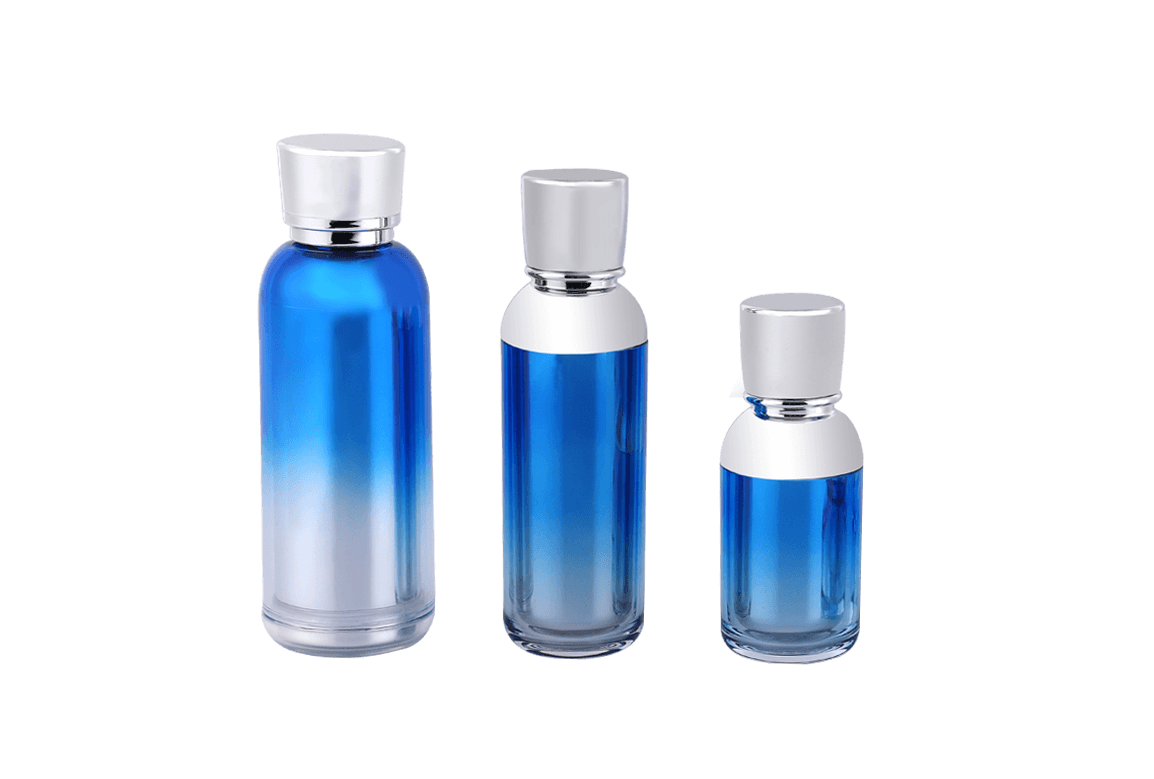
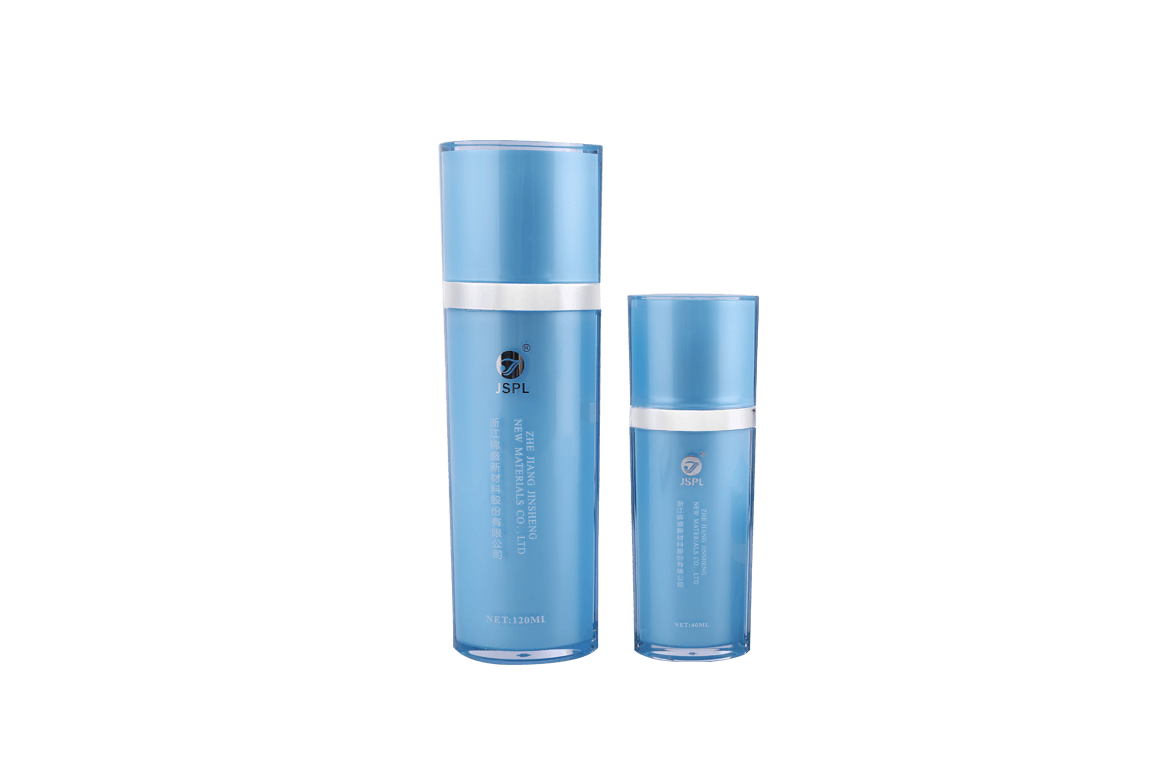
Different types of plastics exhibit varying chemical resistance and compatibility with cosmetic formulations. Common types of plastics used for cosmetic jars include:
Polyethylene (PE): PE is known for its excellent chemical resistance and is commonly used for a wide range of cosmetic products. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers better chemical resistance than low-density polyethylene (LDPE).
Polypropylene (PP): PP is another popular choice due to its chemical resistance, making it suitable for a broad spectrum of cosmetic formulations.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE): PET is commonly used for transparent or semi-transparent cosmetic jars. While it has good chemical resistance, it may not be ideal for certain aggressive formulations.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC is used less frequently for cosmetic jars due to concerns about certain chemical additives that can be present in PVC formulations.
Polystyrene (PS): PS is less commonly used for cosmetic jars due to its limited chemical resistance and fragility.
Matching Plastic Material with Cosmetic Formulation:
Cosmetic manufacturers must carefully match the plastic material used in the cosmetic jar with the specific formulation of the product. Certain ingredients, such as essential oils, solvents, or active compounds, can interact with some plastics, leading to potential issues like leaching, degradation, or alteration of the product.
Preserving Product Efficacy:
Chemical compatibility is crucial for preserving the efficacy and stability of the cosmetic product. When a formulation interacts with the packaging material, it may lead to contamination or degradation, affecting the product's performance and shelf life.
Preventing Leaching and Migration:
Leaching is a phenomenon where substances from the plastic material can migrate into the cosmetic product. For instance, certain plasticizers, like phthalates, can leach from plastic containers and contaminate the product. Selecting a plastic with good chemical compatibility helps minimize the risk of leaching and migration.

 Chinese
Chinese España
España Italia
Italia Le français
Le français